
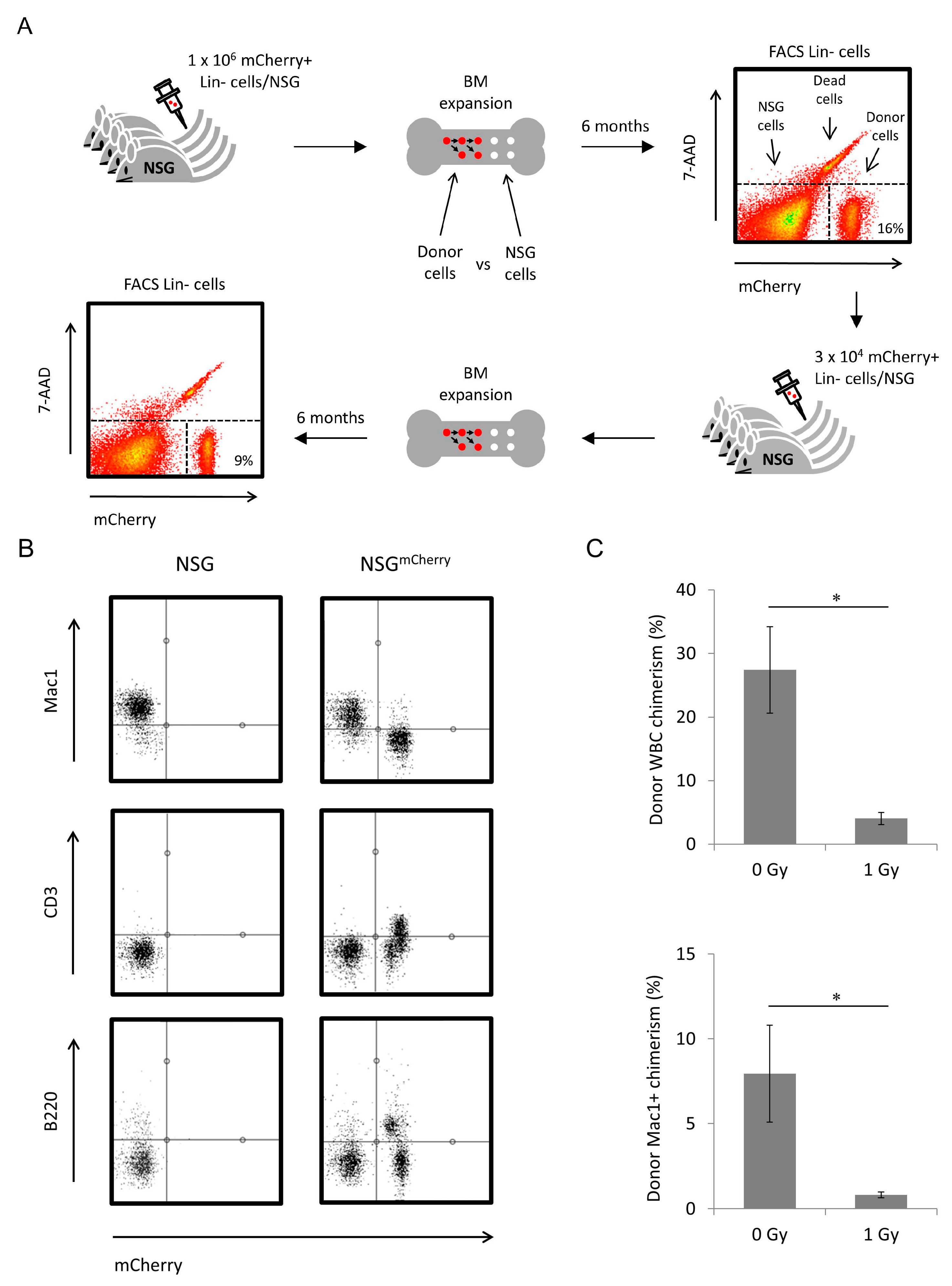
Finally, cDNA microarray analyses indicated that ∼95% of genes were expressed at similar levels in human AML cells immunopurified after growth in mice, as compared to cells assessed directly from patients.
#Nod scid gamma mice serial#
One passage of human AML cells in NOD/SCID mice did not appear to select for increased virulence, as measured by serial transplantation efficiency.

Nevertheless, AML cells obtained from patients at relapse did not engraft more efficiently than cells obtained from the same patients at initial diagnosis. Cases with poor prognosis clinical features, including FLT3 mutations, tended to engraft efficiently. Intravenous transfer of as few as 10 5 human AML cells resulted in engraftment.
#Nod scid gamma mice full#
There is no full text article associated with this abstract published in The FASEB Journal.Most cases of human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) engraft in irradiated non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mice. This abstract is from the Experimental Biology 2019 Meeting. Additional support provided by The Ohio State University Graduate School. Future challenge studies with additional non-mouse-adapted IAVs will help clarify this phenomenon and establish the limitations of their use in humanized mouse models of anti-IAV immunity.įederal funds from Centers of Excellence for Influenza Research and Surveillance, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services, under contract number HHSN272201400006C were used for this work. While this contradicts the general consensus that IAV is not naturally infectious in mice, there are key differences between H1 and H3 subtype IAVs suggesting HA subtype influences infection. These findings support the general potential of non-mouse-adapted IAV isolates to cause clinical and microscopic disease in NSG mice. In contrast, the pulmonary pathology in H3 IAV-challenged mice ranged from mild to absent. Pulmonary lesions and immunohistochemical (IHC) labeling in all H1 IAV-challenged mice (n=8) were consistent with IAV infection, and lesions were most severe in this group. Microscopic lung lesions included acute airway epithelial degeneration and necrosis, acute peribronchial/bronchiolar inflammation, consolidation, and hemorrhage. H1 subtype IAVs caused rapid weight loss in challenged mice at 96 hours post-infection (mean decrease 14.1% body weight) as compared to H3 subtype IAV-challenge and control mice, which showed no significant weight loss. Infectious virus was recovered from the lungs of all virus-challenged NSG mice (n=14). Lungs were split: viral quantification was performed via endpoint dilution assay, and virus-associated pathology was assessed via microscopic examination of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues. Animals were observed for 96 hours post-challenge prior to euthanasia and postmortem tissue collection.
Pairs of adult NSG mice were intranasally inoculated with one of seven IAVs (10 5–10 6 TCID 50 in 50uL PBS) or sterile PBS. We hypothesized that NSG mice would be naturally susceptible to infection with non-mouse-adapted human- and swine-origin hemagglutinin subtype 1 (H1) and H3 IAVs. Our objective was to investigate the susceptibility of the immunodeficient 2rg−/− (NSG) mouse strain to infection with non-mouse-adapted human- and swine-origin IAVs. Further, use of mouse-adapted IAVs may not accurately reflect antigenic and pathologic features of non-mouse-adapted viruses. However, it is widely accepted that IAV infection in mice requires serial passage, though the natural susceptibility of immunodeficient mice is unclear. The ability to use humanized mouse models incorporating natural anti-IAV immunity could advance current pandemic risk assessment strategies. Investigation of human population immunity against swine-origin IAVs identified at the animal-human interface is critical to understanding the risk associated with these viruses.

Influenza A viruses (IAV) emerging from animal reservoirs pose pandemic influenza threat.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
